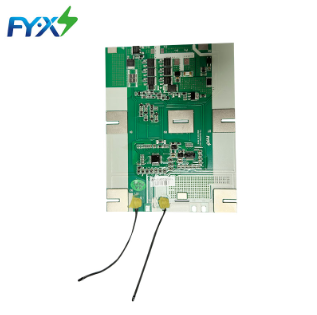
10S 36V BMS 15A Lithium Battery for E-scooter
As the professional 10S 36V BMS 15A Lithium Battery for E-scooter manufacture,empower your E-scooters with FY•X’s efficient 10S 36V BMS, delivering a robust 15A Lithium Battery solution. Connect with our reliable suppliers in China to elevate your electric scooters with superior performance and cutting-edge technology.
Model:Fish10S005
Product Description
This FY•X advanced 10S 36V BMS 15A Lithium Battery for E-scooter is a protective board solution specially designed by Huizhou Feiyu New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. for 10-cell battery packs such as electric bicycles and scooters. It can be applied to lithium batteries with different chemical properties, such as lithium ion, lithium polymer, etc. The protection board has strong load capacity, and the maximum continuous current can be 15A.
FY•X advanced 10S 36V BMS 15A Lithium Battery for E-scooter Functional characteristics
● Ten battery cells are protected in series;
● Charging and discharging voltage, temperature, overcurrent and other protection functions;
● Low power consumption.
Physical reference picture

Figure 1: BMS front view

Figure 2: Physical picture of the back of BMS
Electrical Characteristic (Ta = 25 ℃.)
| Details | Min. | Typ. | Max | Error | Unit | ||||
| Battery | |||||||||
| Battery Gas | LiCoxNiyMnzO2 | ||||||||
| Battery Links | 10S | ||||||||
| Absolute Maximum Rating | |||||||||
| Input Charging Voltage | 42 | ±1% | V | ||||||
| Input Charging Current | 1.5 | 2.5 | A | ||||||
| Output Discharging Voltage | 28 | 36 | 42 | V | |||||
| Output Discharging Current | 7 | 15 | A | ||||||
| Continuous Output Discharging Current | ≤15 | A | |||||||
| Ambient Condition | |||||||||
|
Operating Temperature |
-20 | 75 | ℃ | ||||||
| Humidity (No Water-Drop) | 0% | RH | |||||||
| Storage | |||||||||
| Temperature | -40 | 85 | ℃ | ||||||
| Humidity (No Water-Drop) | 0% | RH | |||||||
| Protection Parameters | |||||||||
| Over-Charge Voltage Protection | 4.200 | 4.250 | 4.300 | ±50mV | V | ||||
| Over-Charge Voltage Protection Delay Time
过充电保护延时1 |
500 | 1000 | 2000 | ms | |||||
| Over-Charge Voltage Protection Release | 4.070 | 4.15 | 4.230 | ±80mV | V | ||||
| Over-Charge Voltage Protection | 4.200 | 4.250 | 4.300 | ±50mV | V | ||||
| Over-Charge Voltage Protection Delay Time | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | ms | |||||
| Over-Charge Voltage Protection Release | 4.070 | 4.150 | 4.230 | ±80mV | V | ||||
| Over-Discharge Voltage Protection | 2.700 | 2.800 | 2.900 | ±100mV | V | ||||
| Over-Discharge Voltage Protection Delay Time | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | ms | |||||
| Over-Discharge Voltage Protection Release | 2.900
And disconnect the load or charge |
3.000And disconnect the load or charge | 3.100
And disconnect the load or charge |
±100mV | V | ||||
| Over-Discharge Voltage Protection | 2.400 | 2.500 | 2.600 | ±100mV | V | ||||
| Over-Discharge Voltage Protection Delay Time | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | ms | |||||
| Over-Discharge Voltage Protection Release | 2.900
And disconnect the load or charge |
3.000And disconnect the load or charge | 3.100And disconnect the load or charge | ±100mV | V | ||||
| Charge overcurrent protection | 7 | 10 | 13 | ±3 | A | ||||
| Charge overcurrent protection delay | 250 | 500 | 1000 | ms | |||||
| Charging overcurrent protection release | automatic release | ||||||||
| Discharge overcurrent 1 protection | 44 | 50 | 56 | ±6 | A | ||||
| Discharge overcurrent 1 protection delay | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | ms | |||||
| Discharge overcurrent 1 protection release | Disconnect load or charge | ||||||||
| Discharge overcurrent 2 protection | 88 | 100 | 112 | ±12 | A | ||||
| Discharge overcurrent 2 protection delay | 130 | 100 | 150 | ±50 | ms | ||||
| Discharge overcurrent 2 protection release | Disconnect load or charge | ||||||||
| Short circuit protection | 250 | 600 | A | ||||||
| Short circuit instructions | Short circuit description: The short circuit current is less than the minimum value or higher than the maximum value
value may cause the short-circuit protection to fail and the short-circuit current to exceed 600A, short circuit protection is not guaranteed, and short circuiting is not recommended. road protection test |
||||||||
| Short circuit protection delay | 200 | 350 | 600 | us | |||||
| Short circuit protection release | Disconnect load or charge | ||||||||
| Level 1 charging high temperature protection | 45 | 50 | 55 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 1 charging high temperature protection release | 40 | 45 | 50 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 charging high temperature protection | 47 | 52 | 57 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 charging high temperature protection release | 42 | 47 | 52 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 1 charging low temperature protection | -7 | -2 | 3 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 1 charging low temperature protection release | -2 | 3 | 8 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 charging low temperature protection | -10 | -5 | 0 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 charging low temperature protection release | -5 | 0 | 5 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 1 discharge high temperature protection | 65 | 70 | 75 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 1 discharge high temperature protection release | 55 | 60 | 65 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 discharge high temperature protection | 65 | 73 | 75 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 discharge high temperature protection release | 60 | 68 | 70 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 1 discharge low temperature protection | No such function | ||||||||
| Level 2 discharge low temperature protection | -30 | -25 | -20 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Level 2 discharge low temperature protection release | -25 | -20 | -15 | ±5 | ℃ | ||||
| Current Consumption | |||||||||
| SleepConsumption | 100 | 130 | uA | ||||||
| Overall undervoltage power consumption | 60 | 80 | uA | ||||||
values and users can modify them according to actual applications.
Note: The level 1 temperature protection release of charging is automatically released after the temperature reaches the release level, and the level 2 protection release is to disconnect the charger;
The discharge level 1 temperature protection is released after the temperature reaches the release level and the load is disconnected. The level 2 temperature protection release is automatically released after the temperature recovers;
BMS principle block diagram

Figure 7: Protection principle block diagram
PCB and dimensional structure diagram

Figure 8: Motherboard top-level wiring diagram

Figure 9: Motherboard bottom wiring diagram

Figure 10: Dimensions 108.5*140 Unit: mm Tolerance: ±0.5mm
Protection board thickness: less than 10mm (including components)
Port Definition

Figure 11: Protection board wiring diagram
Port definition description::
| Item | Details | ||
| B+ | Connect to Positive Side of the pack. | ||
| B- | Connect to Negative Side of the pack. | ||
| P- | Discharging Negative Port. | ||
| C- | Charging Negative Port . | ||
| J1 | 1 | B- | Connect to Negative Side of Cell 1. |
| 2 | B1 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 1. | |
| 3 | B2 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 2. | |
| 4 | B3 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 3. | |
| 5 | B4 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 4. | |
| 6 | B5 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 5. | |
| 7 | B6 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 6. | |
| 8 | B7 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 7. | |
| 9 | B8 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 8. | |
| 10 | B9 | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 9. | |
| 11 | B+ | Connect to Positive Side of Cell 10. | |
| NTC1 | Level 1 Temperature Probe | ||
| NTC2 | Level 2 Temperature Probe | ||

Figure 12: Schematic diagram of battery connection sequence
Precautions for connecting the protective board and the battery core
Warning: When connecting the protective plate to the battery cells or removing the protective plate from the battery pack, the following connection sequence and regulations must be followed; if operations are not performed in the required order, the components of the protective plate will be damaged, resulting in the protective plate being unable to protect the battery. core, causing serious consequences.
Preparation: According to the definition shown in Figure 11, connect the corresponding voltage detection cable to the corresponding battery core. Please pay attention to the order in which the sockets are marked.
Steps to install protective board:
Step 1: Weld the P- and C- wires to the corresponding positions of the protection board without connecting the charger and load.
Step 2: Connect the negative pole of the battery pack to B- of the protection board;
Step 3: Connect the positive terminal of the battery pack to B+ of the protection board;
Step 4: Connect the battery cells B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 in sequence;
Steps to remove the protective plate:
Step 1: Disconnect all chargers\loads
Step 2: Disconnect the battery cells B9, B8, B7, B6, B5, B4, B3, B2, B1 in sequence;
Step 3: Remove the connecting wire connecting the positive electrode of the battery pack from the B+ pad of the protective plate
Step 4: Remove the connecting wire connecting the negative electrode of the battery pack from the B- pad of the protective plate
Additional notes: Please pay attention to electrostatic protection during production operations.
BOM list of main components
| Device type | model | encapsulation | brand | Dosage | Location | |
| 1 | Chip IC
|
PT6010EL32-AB | TQFP32 | China Resources Micro
|
1PCS | U1 main selection |
| PT6010EL32-AA | alternative | |||||
| 2 | Chip IC | CW1102ALAS | SSOP20 | Saiwei | 1PCS | U4 |
| 3 | MOS tube
|
CRTD082NE6N | TO252 | China Resources Micro | 8PCS | MC1 MC2 MD1 MD2 MD3 MD4 MD5 MD6 |
| WMO80N06TS | Vian | |||||
| TTD95N68A | Ziguangwei | |||||
| 4 | PCB | Fish10S005 V1.0 | 108.5*140*1.6mm | 1PCS |
Ordering information

1 Huizhou Feiyu New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. logo;
2 Protection board model – (This protection board model is Fish10S001, other types of protection boards are marked, there is no limit to the number of characters in this item)
3. The number of battery strings supported by the required protection board – (this model of protection board is suitable for 17S battery packs);
4 Charging current value – 2A means the maximum support for continuous 2A charging;
5 Discharge current value – 20A means the maximum support for continuous charging is 20A;
6 Balance resistance size – fill in the value directly, for example, 100R, then the balance resistance is 100 ohms;
7 Battery type – one digit, the specific serial number indicates the battery type as follows;
| 1 | Polymer |
| 2 | LiMnO2 |
| 3 | LiCoO2 |
| 4 | LiCoxNiyMnzO2 |
| 5 | LiFePO4 |
8 Communication method – one letter represents a communication method, I represents IIC communication, U represents UART communication, R represents RS485 communication, C represents CAN communication, H represents HDQ communication, S represents RS232 communication, 0 represents no communication, and the product UC represents UART+CAN dual communication;
9 Hardware version – V1.0 means the hardware version is version 1.0.
10 The model number of this protection board is: FY-Fish10S005-10S-2A-15A-0-4-0-V1.0. Please place the order according to this model number when placing bulk orders.
Additional notes:
1. When performing charge and discharge tests on the battery pack with the protective board installed, please do not use the battery aging cabinet to measure the voltage of each cell in the battery pack, otherwise there may be
The protective board and battery may be damaged. .
2. This protection board does not have a 0V charging function. Once the battery reaches 0V, the battery performance will be seriously degraded and may even be damaged. In order not to
If the battery is damaged, the user needs to charge it regularly to replenish the power when not in use for a long period of time (battery pack capacity is greater than 15AH, storage exceeds 1 month); and
After being discharged during use, it must be charged in time within 12 hours to prevent the battery from being discharged to 0V due to self-consumption. Customers are required to have a clear label on the battery casing.
Display the user’s instructions for regular maintenance of the battery.
3. This protection board does not have reverse charging protection function. If the polarity of the charger is reversed, the protection board may be damaged.
4. This protective board shall not be used in medical products or products that may affect personal safety.
5. Our company will not be responsible for any accidents caused by the above reasons during the production, storage, transportation and use of the product.
6. This specification is a performance confirmation standard. If the performance required by this specification is met, our company will change some materials according to the order materials.
The model or brand of the material will not be notified separately.
7. The short-circuit protection function of this management system is suitable for a variety of application scenarios, but it does not guarantee that it can be short-circuited under any conditions. When the battery pack and short circuit
The total internal resistance of the loop is less than 40mΩ, the battery pack capacity exceeds the rated value by 20%, the short-circuit current exceeds 1500A, and the inductance of the short-circuit loop is very
When the total length of large or short-circuited wires is very long, please test by yourself to determine whether this management system can be used.
8. When welding battery leads, there must be no wrong connection or reverse connection. If it is indeed connected incorrectly, the circuit board may be damaged and needs to be retested to pass the test.
It can be used later.
9. During assembly, the management system should not directly contact the surface of the battery core to avoid damaging the circuit board. The assembly must be firm and reliable.
10. During use, be careful not to touch the lead tips, soldering iron, solder, etc. on the components on the circuit board, otherwise the circuit board may be damaged.
Pay attention to anti-static, moisture-proof, waterproof, etc. during use.
11. Please follow the design parameters and usage conditions during use, and the values in this specification must not be exceeded, otherwise the management system may be damaged. Place the battery pack
After being combined with the management system, if you find no voltage output or no power when powering on for the first time, please check whether the wiring is correct.
Note: After your company receives the prototype and specifications, please reply promptly. If there is no reply within 7 days, our company will regard your company as having recognized the specifications and send the prototype. If your order exceeds 50 PCS, you need to sign back the acknowledgment letter. If you do not sign back, our company will also regard your company as having approved this specification and send the sample machine. The pictures in the specification are of general models and may be slightly different from the sample delivered. Huizhou Feiyu New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. reserves the right of final interpretation of this specification.
DISCLAIM:
In order to improve the design or performance and to supply the best possible products, Feiyuxinneng reserves the right to make changes to the products contained in this data sheet. Feiyuxinneng assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuits shown in this data sheet, conveys no license under any patent or other rights, and makes no claim that the circuits are free from patent infringement. Applications for any devices shown in this data sheet are for illustration only and Feiyuxinneng makes no claim or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the use specified without further testing or modification.
LIFE RELATED POLICY:
In situations where semiconductor component failure may endanger life, system designers using this product should design the system with appropriate error detection and correction, redundancy and back-up features to prevent such an occurrence.
Feiyuxinneng’s products are not authorized for use in critical components in life support devices or systems.
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform, when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.